Tert-butyl alcohol, also known as tert-butanol, is a solvent that can be used in the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction, a chemical process that involves the alkylation of aromatic rings. The reaction typically requires a catalyst, and various catalysts have been investigated for use in the Friedel-Crafts alkylation with tert-butyl alcohol, including solid acid catalysts such as UDCaT-5 and Fe2O3-modified Hβ. The choice of catalyst and reaction conditions can impact the selectivity and yield of the desired products.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Catalyst | UDCaT-5 |
| Alkylating agents | Methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) and tert-butanol |
| Conversion of tert-butanol | 94% |
| Reaction temperature | 120–150 °C |
| Solvent | None |
What You'll Learn

Friedel-Crafts Alkylation of Mesitylene with tert-Butyl Alcohol
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation of mesitylene with tert-butyl alcohol was studied using a novel solid acid catalyst called UDCaT-5. The catalyst was developed to produce 2-tert-butyl-mesitylene (2-TBMT) with high selectivity and conversion rates. The formation of products was correlated with the acidity of the catalyst, and the reactions were conducted in the liquid phase at low temperatures of 120-150 °C.
The study focused on investigating the effects of various operating parameters and developing a mathematical model to describe the reaction pathway. The reaction was carried out without any solvent to make the process cleaner and more environmentally friendly. The synergistic effect of the high sulfur content (9% w/w S) and the preservation of the tetragonal phase in UDCaT-5 contributed to its higher catalytic activity compared to sulfated zirconia.
In the study, several solid acids were evaluated, with dodecatungstophosphoric acid/K10 montmorillonite clay (DTP/K10) showing the most activity for the alkylation of aniline with both methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) and tert-butanol. The yield of mono-alkylated products was over 84% with a selectivity of 53% towards 2-tert-butylaniline using MTBE. With tert-butanol, only mono-alkylated products were obtained at 150°C with equal isomer distribution.
The performance of UDCaT-5 in the alkylation of xylenes with tert-butanol was also examined. Under optimum reaction conditions, alkylation of m-xylene over UDCaT-5 resulted in a 96% conversion of tert-butanol with 82% selectivity towards 5-tert-butyl-m-xylene (5-TBMX). This study highlights the potential of UDCaT-5 as an effective catalyst for Friedel-Crafts alkylation reactions, offering high selectivity and conversion rates while eliminating the need for solvents.
Hydrogen Peroxide vs Alcohol for Swimmer's Ear
You may want to see also

UDCaT-5 catalyst for high conversion rates
The UDCaT-5 catalyst is a novel mesoporous superacidic catalyst that exhibits remarkable activity, selectivity, and stability for the alkylation of benzene using 1-dodecene. It is a modified version of zirconia, and its high catalytic activity can be attributed to its high sulfur content (9% w/w S) and the preservation of the tetragonal phase.
In the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of xylenes with tert-butanol, UDCaT-5 showed the highest catalytic activity among the catalysts tested, which included UDCaT-4, UDCaT-6, and sulfated zirconia. Under optimal conditions, UDCaT-5 achieved a 96% conversion of tert-butanol and 82% selectivity towards the desired product, 5-tert-butyl-m-xylene.
The superior performance of UDCaT-5 in this reaction can be attributed to its high sulfur content and the preservation of the tetragonal phase, which results in a synergistic effect that enhances its catalytic activity. Kinetic studies found the reaction to be second-order with respect to both xylene and tert-butanol.
UDCaT-5 has also been used in the Friedel-Crafts propionylation of veratrole to 3,4-dimethoxypropiophenone. This reaction is of considerable commercial importance due to its use in the fine chemical and drug industries. UDCaT-5 was found to be the most active and selective catalyst among UDCaT-4, UDCaT-5, and UDCaT-6 in this reaction as well.
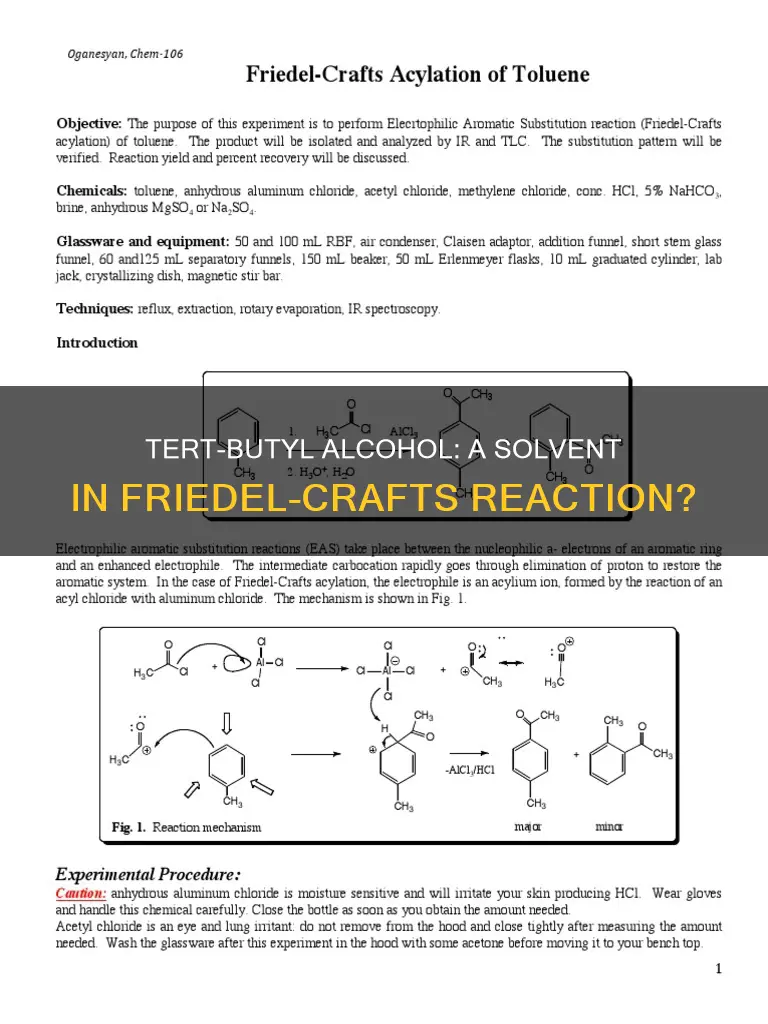
The Friedel-Crafts reaction typically employs a strong Lewis acid, such as aluminium chloride (AlCl3), as a catalyst to increase the electrophilicity of the alkylating agent. However, in the case of the Friedel-Crafts alkylation, the catalyst is constantly regenerated, and a stoichiometric amount of the catalyst is not required. The regeneration of the catalyst allows it to be used repeatedly in the reaction, contributing to its high conversion rates.
Your Wedding, Your Rules: Alcohol-Free Celebrations
You may want to see also

Toluene as an alkylating agent
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction is a well-known method for introducing an alkyl group into an aromatic compound like toluene. Toluene (C6H5CH3) has a methyl group (-CH3) attached to the benzene ring. This methyl group acts as an activating group, enhancing the electron density of the ring and directing further substitutions to the ortho and para positions.
When toluene undergoes Friedel-Crafts alkylation, the potential products depend on the structure of the alkylating agent. For instance, if ethyl chloride (C2H5Cl) is used, the products are ortho-ethyl toluene and para-ethyl toluene. Similarly, using isopropyl bromide (C3H7Br) yields ortho-isopropyl toluene and para-isopropyl toluene.
In the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of toluene with methyl chloride (CH3Cl) in the presence of aluminium chloride (AlCl3), the major product is meta-substituted. This reaction involves the formation of a C-C bond between the aromatic ring and the alkyl halide, facilitated by the strong Lewis acid AlCl3.
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation of toluene has been studied with various catalysts, such as Fe2O3 (x)/Hβ, to understand the effects on channel structures, acidity, and catalytic performance. These studies have shown that modifying the catalyst can adjust pore structures and decrease acidity. For example, the Fe2O3 (x)/Hβ catalyst yielded a toluene conversion of 58.4% with a PTBT selectivity of 67.3%.
In summary, toluene is a key reactant in Friedel-Crafts alkylation reactions, where the choice of alkylating agent and catalyst significantly impacts the products and reaction kinetics.
Handwashing: Soap and Water vs. Alcohol-Based Solutions
You may want to see also

tert-Butyl alcohol as a solvent
Tert-butyl alcohol, also known as tert-butanol, is a solvent used in a variety of chemical processes. It is often employed as a co-solvent or in combination with other solvents to achieve specific outcomes. In the context of Friedel-Crafts alkylation reactions, tert-butyl alcohol serves as an alkylating agent rather than a solvent. However, its role in these reactions highlights its versatility in chemical processes.
In Friedel-Crafts alkylation, tert-butyl alcohol reacts with aromatic compounds to introduce the tert-butyl group. This reaction is facilitated by catalysts, such as UDCaT-5, which enhance the reactivity and selectivity of the process. The choice of catalyst influences the yield and specific product distribution. For example, in the alkylation of mesitylene, the UDCaT-5 catalyst promotes the formation of 2-tert-butyl-mesitylene with high selectivity and conversion rates.
Tert-butyl alcohol is a valuable solvent in various chemical reactions beyond Friedel-Crafts alkylation. It is used in the synthesis of tert-butylated phenols, which are important precursors in multiple industries. Additionally, it plays a role in the production of amides through aminolysis or ammonolysis processes, where it can serve as an alternative solvent to carbon tetrachloride. The choice between solvents depends on the desired reaction conditions and outcomes.
The versatility of tert-butyl alcohol extends further, as it is also utilised in the formation of clear isotropic monophasic solutions. This process involves creating a homogenous dispersion of lipid components in tert-butyl alcohol/water co-solvent systems. The resulting solution is then sterilised and freeze-dried under specific conditions, demonstrating the adaptability of tert-butyl alcohol in various applications.
In summary, while tert-butyl alcohol may not be specifically employed as a solvent in Friedel-Crafts alkylation reactions, it is a versatile solvent in a range of chemical processes. Its ability to participate in alkylation reactions, as well as its use in synthesis, solvent systems, and biocatalytic reactions, showcases its importance in organic chemistry and industrial applications.
Alcoholic Hepatitis: One Year On
You may want to see also

tert-Butyl alcohol without a solvent
Tert-butyl alcohol (TBA), also known as tert-butanol, is used as a reagent in the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction, a widely used chemical process in organic synthesis. The reaction involves the alkylation of aromatic rings, typically benzene or its derivatives, with alkyl halides or alcohols in the presence of a strong Lewis acid catalyst.
In the context of Friedel-Crafts alkylation, tert-butyl alcohol can be used as an alkylating agent without the need for an additional solvent. This approach not only simplifies the reaction but also aligns with green chemistry principles by reducing the use of potentially harmful solvents.
One specific example of this solvent-free approach is the alkylation of mesitylene with tert-butyl alcohol over a novel solid acid catalyst called UDCaT-5. This catalyst, a modified version of zirconia, exhibits high catalytic activity, stability, and reusability. The reaction conditions are carefully optimized to achieve a high conversion rate of tert-butyl alcohol and a high selectivity towards the desired product, 2-tert-butyl-mesitylene (2-TBMT).
Another illustration of tert-butyl alcohol's role in Friedel-Crafts alkylation without a solvent is the reaction between toluene and tert-butyl alcohol over an Fe2O3-modified Hβ catalyst. By adjusting the loading of Fe2O3, the pore structures and acidity of the catalyst can be controlled, influencing the selectivity and yield of the desired product, 4-tert-butyltoluene.
It is worth noting that while these reactions proceed without an explicit solvent, the reactants themselves, such as tert-butyl alcohol and the aromatic compound, may serve as reaction media or act as solvents in certain cases. The specific conditions and reactants chosen can influence the overall solvent-free nature of the process.
When is it Right to Kick Out an Alcoholic Son?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Tert-butyl alcohol, also known as tert-butanol, is a type of alcohol used in various chemical processes.
Friedel Crafts is a chemical reaction that involves the alkylation of aromatic compounds, typically using an alkyl halide as the alkylating agent.
No, tert-butyl alcohol is not used as a solvent in the Friedel Crafts reaction. Instead, it is used as a reactant or alkylating agent in the presence of a solid acid catalyst, such as UDCaT-5. The reaction is conducted in the liquid phase without the use of any additional solvents.







